In this section
Learn:
- About your state's prescription drug monitoring program (PDMP) and how to integrate data from it
- How to reduce fraud and abuse with electronic prescribing of controlled substances
- How to use smartphone apps to help with opioid prescribing
- How PDMPs fulfill regulatory requirements
- About additional resources on opioids and PDMP
This section of the Playbook provides background on the role health IT plays in fighting the opioid epidemic in the United States. It presents health IT strategies that clinicians can use to address the problem. Healthcare practitioners, administrators and physician practice owners, and practice staff can also find a variety of health IT resources in this section. These strategies and resources can help improve opioid prescribing practices, inform clinical practice, protect patients at risk for opioid use disorder, and reduce diversion.
Learn about:
- Opioid Epidemic from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Providers' Clinical Support System for Opioid Therapies from Providers' Clinical Support System for Opioid Therapies (PCSS-O)
How can health IT help?
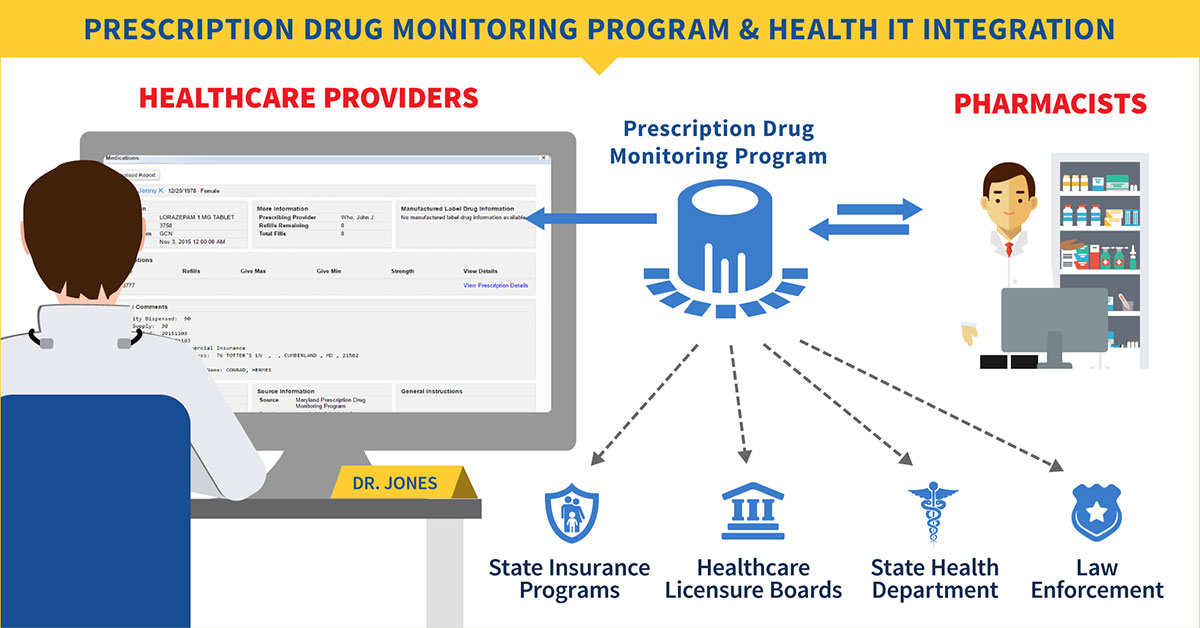
Health IT is increasingly used to improve the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery, patient safety, care coordination, and patient-centered care. This includes offering strategies to address the opioid epidemic. The use of health IT has been demonstrated to improve adherence to opioid prescribing guidelines and physician adherence to treatment protocols, increase the safety of prescribing for controlled substances, enhance clinician access to prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs), expand access to addiction treatment and recovery supports, and much more.
As the opioid epidemic escalates, clinicians are actively seeking tools and resources to help prevent and detect opioid misuse, abuse, and diversion by their patients. The following sections of the Playbook describe in detail how various health IT solutions are being used by clinicians on the frontlines to address the opioid crisis in their practices.