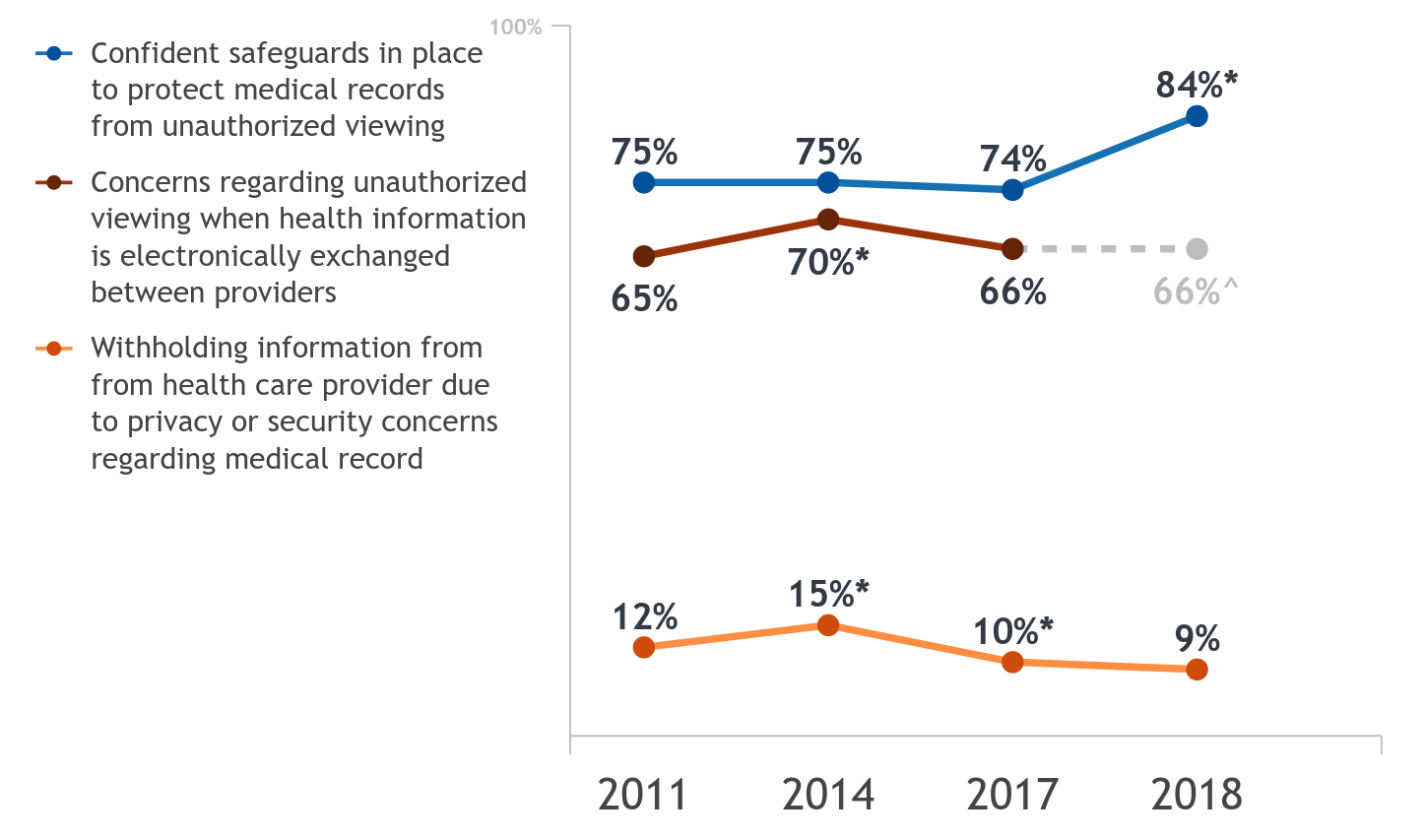
A majority of individuals (84%) are confident their medical records are safe from unauthorized viewing, but have concerns (66%) when health information is electronically exchanged. More individuals are now confident their records are safe from…
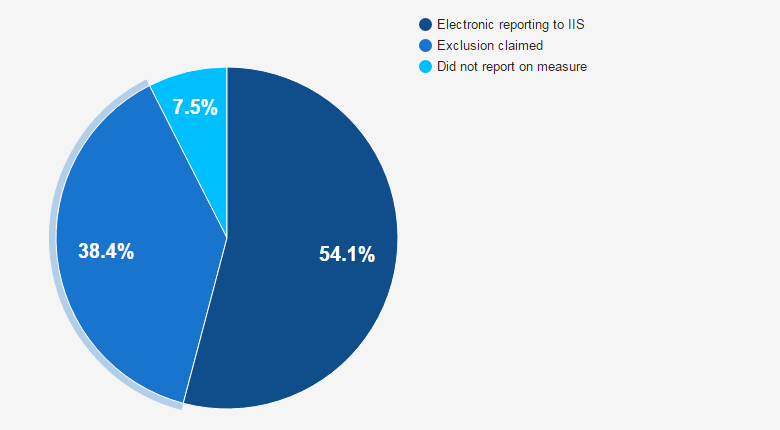
In 2015, 54 percent of eligible professionals (EP) participating in Stage 2 of the Medicare EHR Incentive Program and 44 percent of professionals participating in modified stage 2 electronically reported immunizations to local registries.
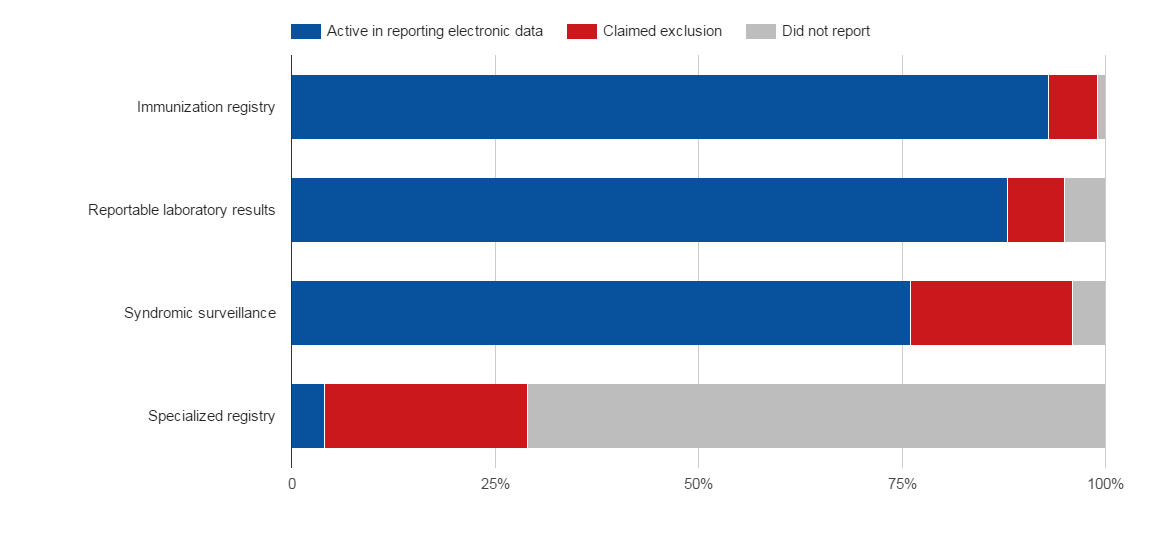
In 2015, 4,043 eligible and Critical Access hospitals (EH) reported to the Medicare EHR Incentive Program. 90 percent of hospitals attested to stage 2 of meaningful use. 93 percent of all hospitals reported active engagement with an immunization registry…
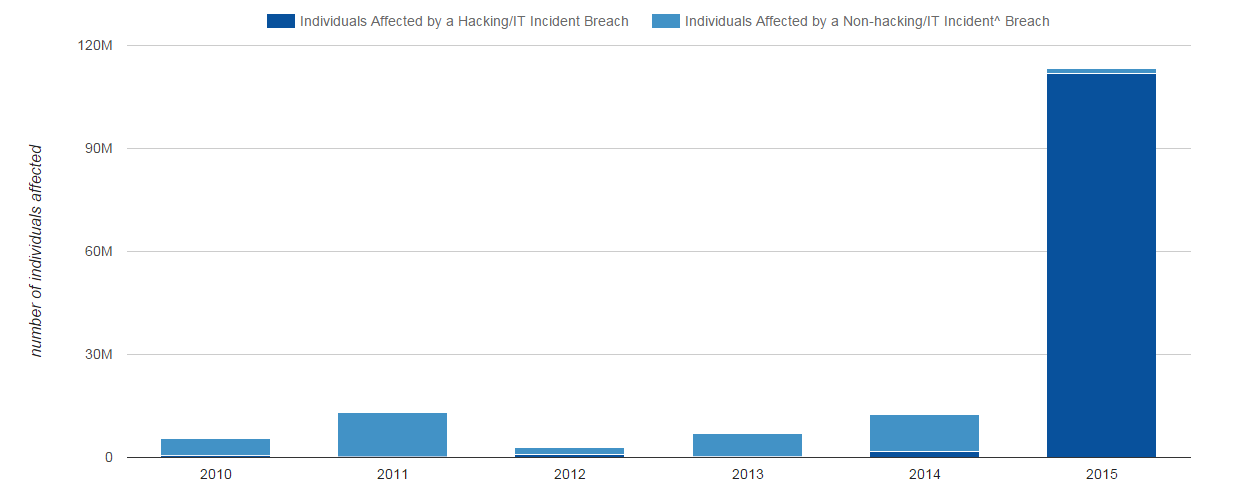
Based upon data collected by the HHS Office for Civil Rights, as of February 1, 2016, protected health information breaches affected over 113 million individuals in 2015. In 2015, hacking incidents comprised nearly 99% of all individuals affected by…
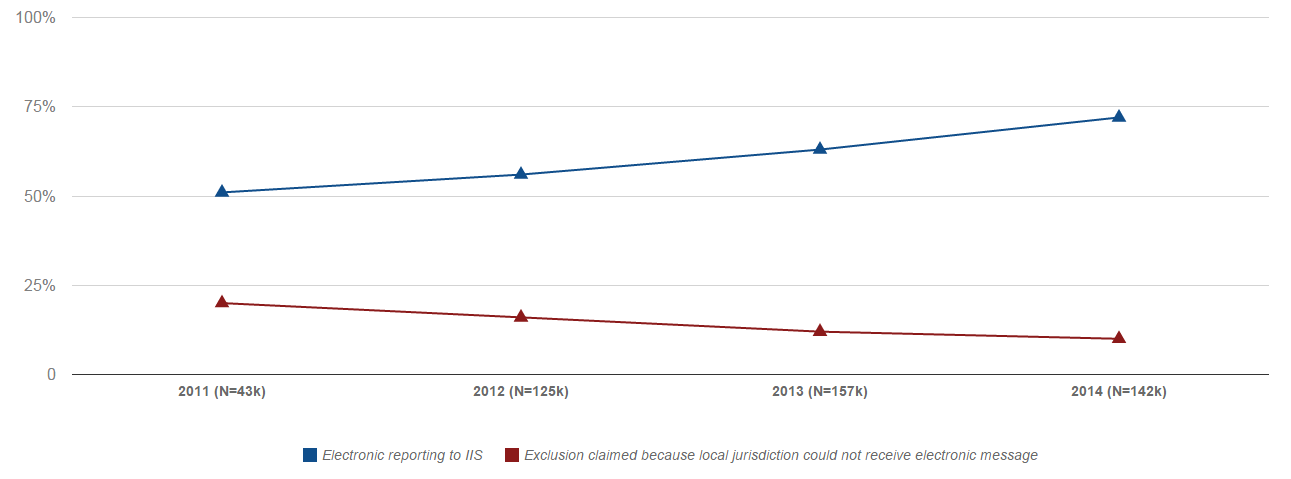
Electronic report to Immunization Information Services (IIS) was an optional measure for participants at stage 1 of the Medicare EHR Incentive Program, and a required measure for stage 2. Since 2011, electronic IIS reporting among eligible professionals…
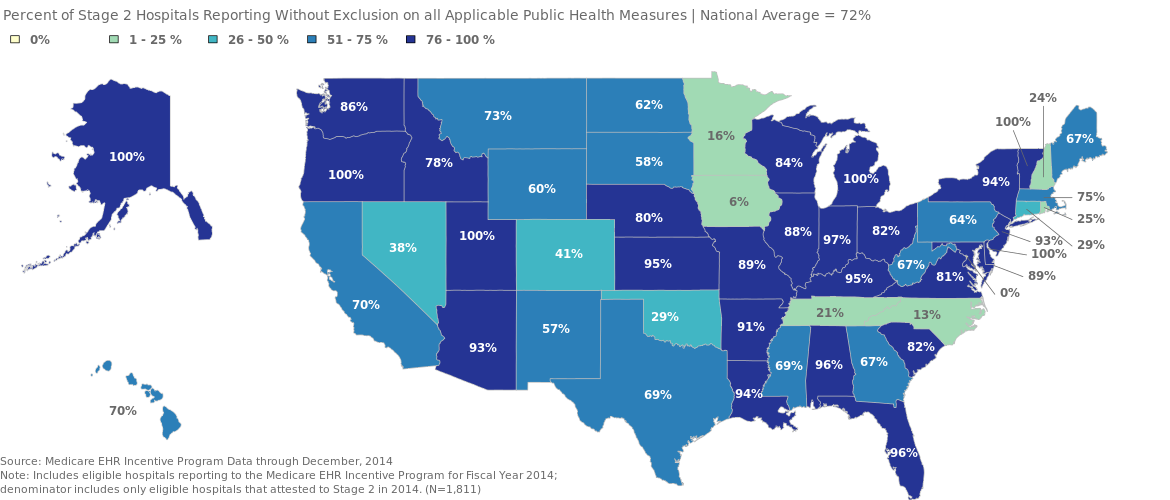
The CMS EHR Incentive Program provides incentive payments for eligible hospitals to adopt and meaningfully use certified health IT. Among the requirements to receive an incentive payment, participating hospitals must report on public health measures.…
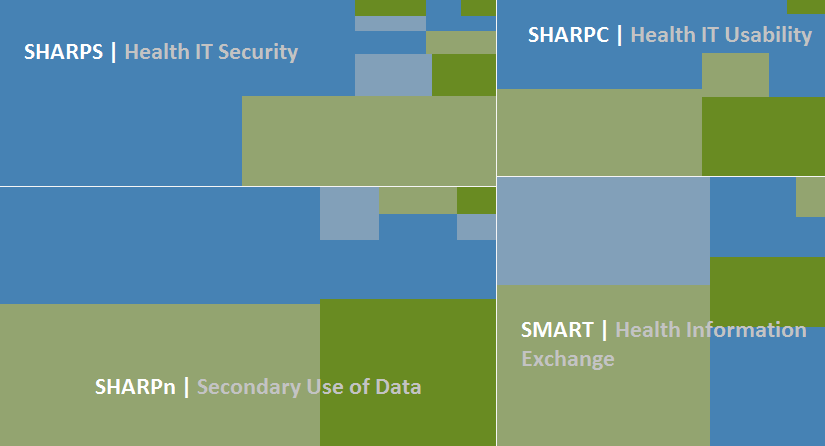
The Office of the National Coordinator for Health IT established the SHARP program to support innovative research and to address well-documented problems that impede the adoption and use of health IT. The SHARP program covers four subject areas:
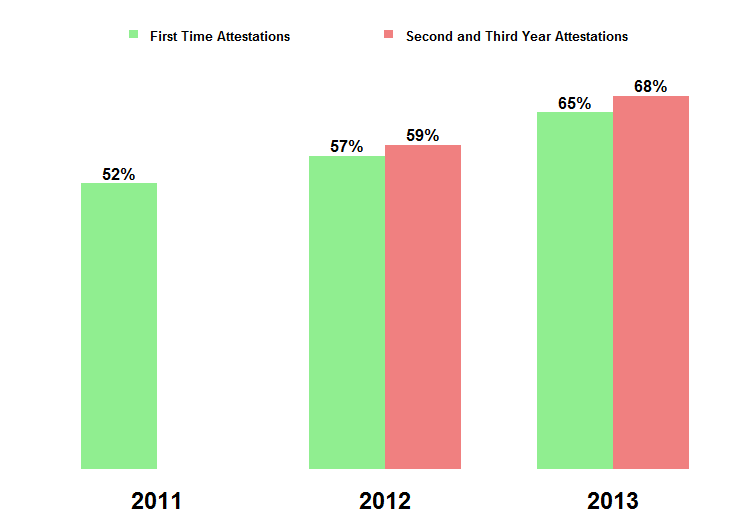
Approximately 7 out of 10 primary care physicians eligible for the Medicare EHR Incentive Program selected the Immunization Meaningful Use Menu measure without exclusion in 2013. 65 percent of 2013 first time attesters selected this measure without…
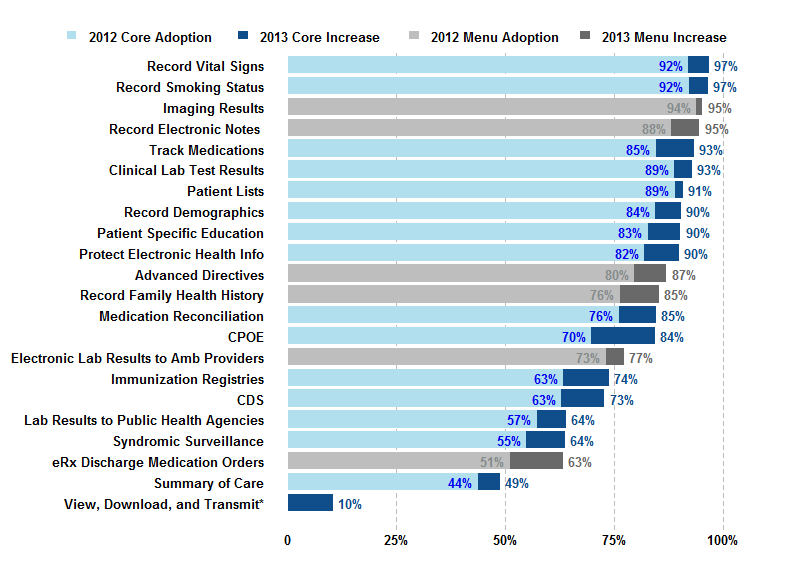
Stage Two of the Meaningful Use program consists of 22 core and menu objectives. A subset of hospitals will be eligible to begin attesting to these Stage 2 objectives in 2014. In 2013, adoption rates for 20 of these objectives were over 60 percent.…
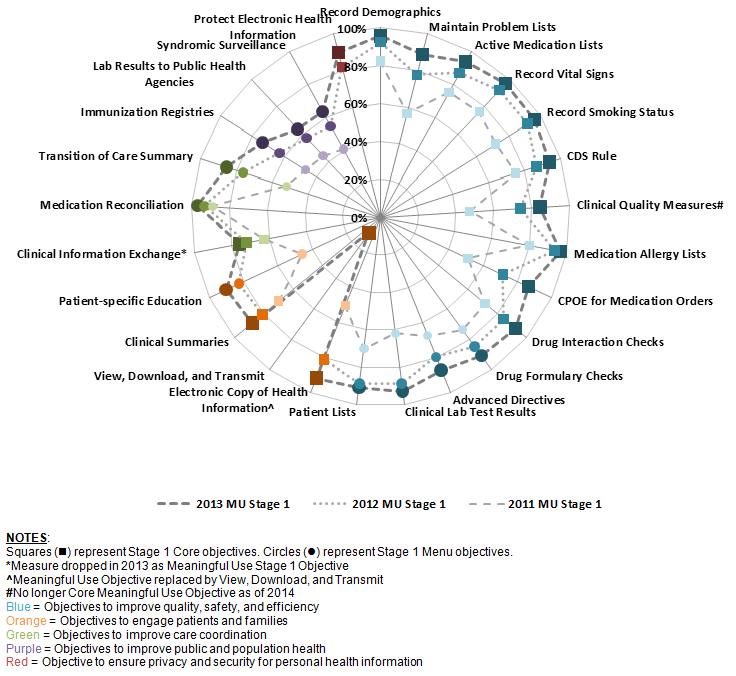
Stage 1 of the Meaningful Use program consists of 24 core and menu objectives. Hospitals began attesting to Stage 1 in 2011.
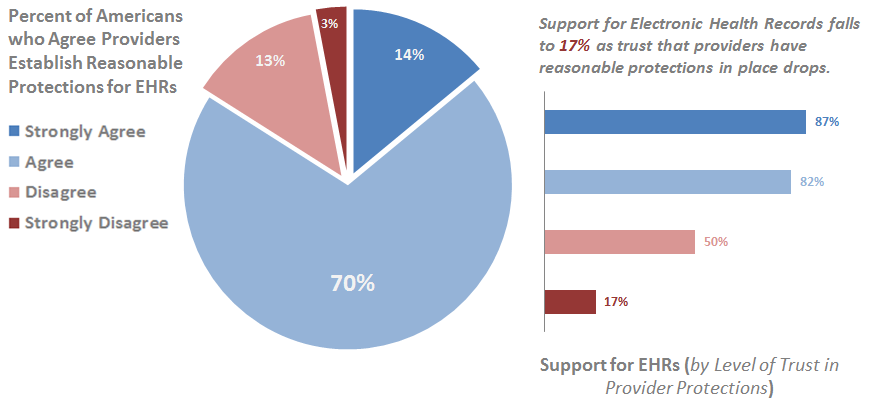
As the adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) and health information exchange (HIE) expands, and patient health information is increasingly stored and shared by providers electronically, it is important to monitor patient trust in providers'…
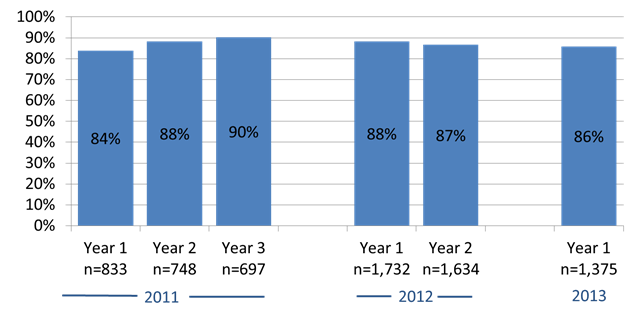
Hospitals that began the Meaningful Use program in 2011 were 6 percentage points more likely to select at least one public health measure without an exclusion by their third year of participation (2013), compared to their first year of participation (…
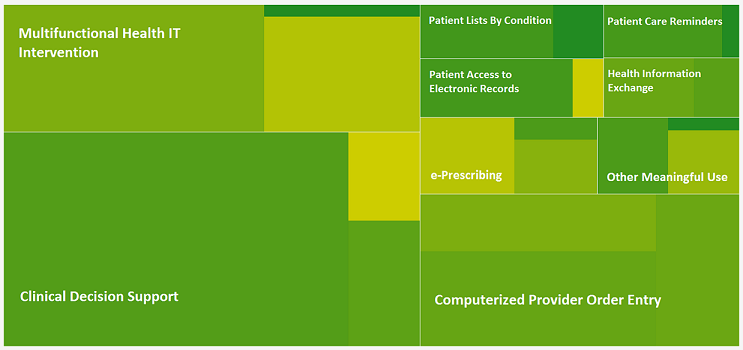
The 'Updated Systematic Review' reviews the January 2010 to August 2013 health IT literature to examine the effects of health IT across three aspects of care -- efficiency, quality, and safety. This report updates previous systematic reviews of…
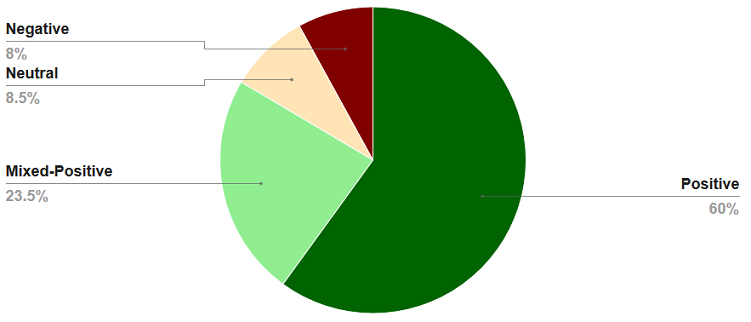
Graphic visualizes Health IT evaluation studies, 2007-2013 (n=493), related to the impact of Meaningful Use functionality on the quality, efficiency, and safety of care (or aspects of care). Positive defined as health IT improved key aspects of care but…
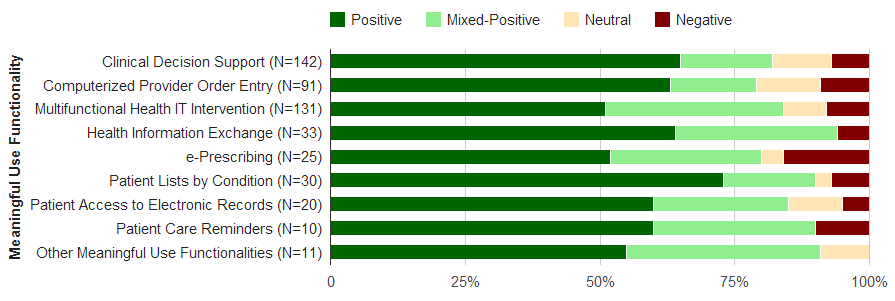
Graphic visualizes Health IT evaluation studies, 2007-2013 (n=493), related to the impact of Meaningful Use functionality on the quality, efficiency, and safety of care (or aspects of care). Positive defined as health IT improved key aspects of care but…
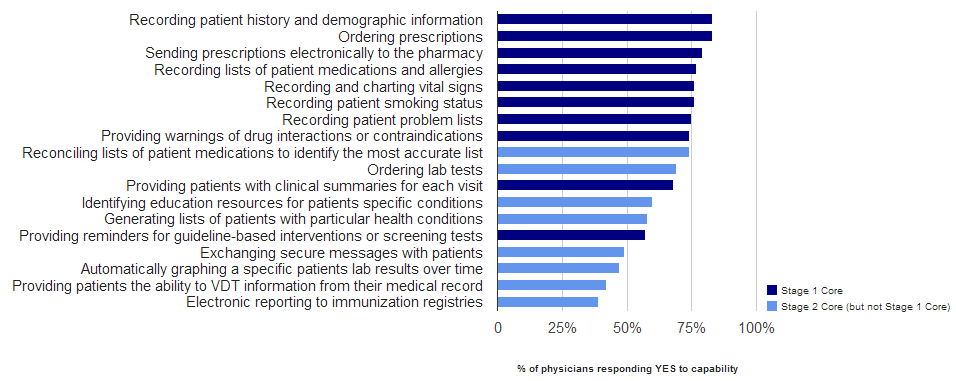
In 2013, physician adoption rates for computerized capabilities related to selected Meaningful Use Stage 1 and Stage 2 objectives ranged from 39% to 83%. About three-quarters or more of physicians had adopted computerized capabilities for recording key…
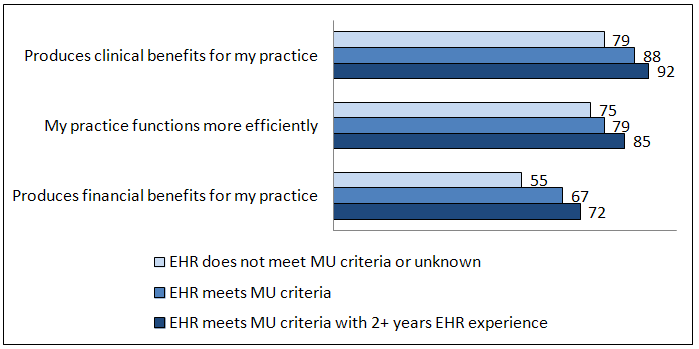
The majority of office-based physicians with electronic health records (EHR) reported their EHRs had clinical, efficiency, and financial benefits for their practice. Physicians with EHRs meeting meaningful use (MU) criteria were more likely to report…
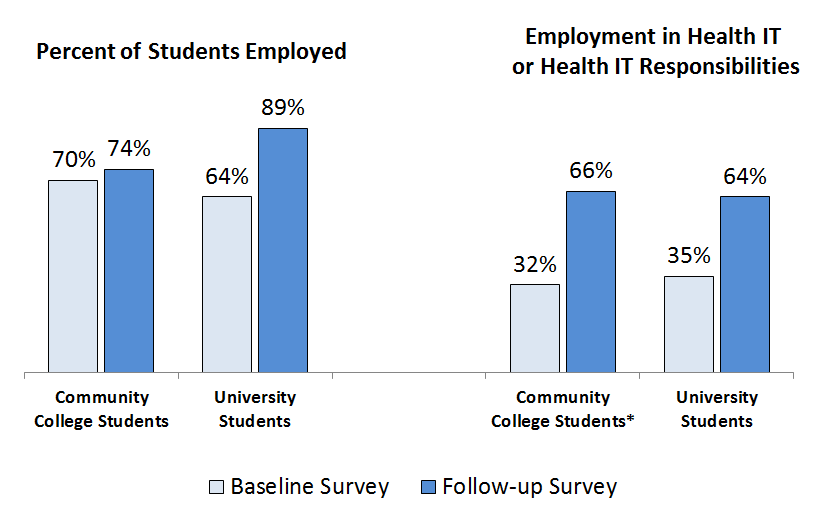
Over three-fourths of students trained by the HITECH Workforce Programs were employed within six months of completing training. Moreover, two-thirds of all trained professionals were employed in health IT or had health IT related responsibilities.

